Fraud & Scams
- Sizing Exposures
- Identification & Tips
- Internal Controls
- Actions

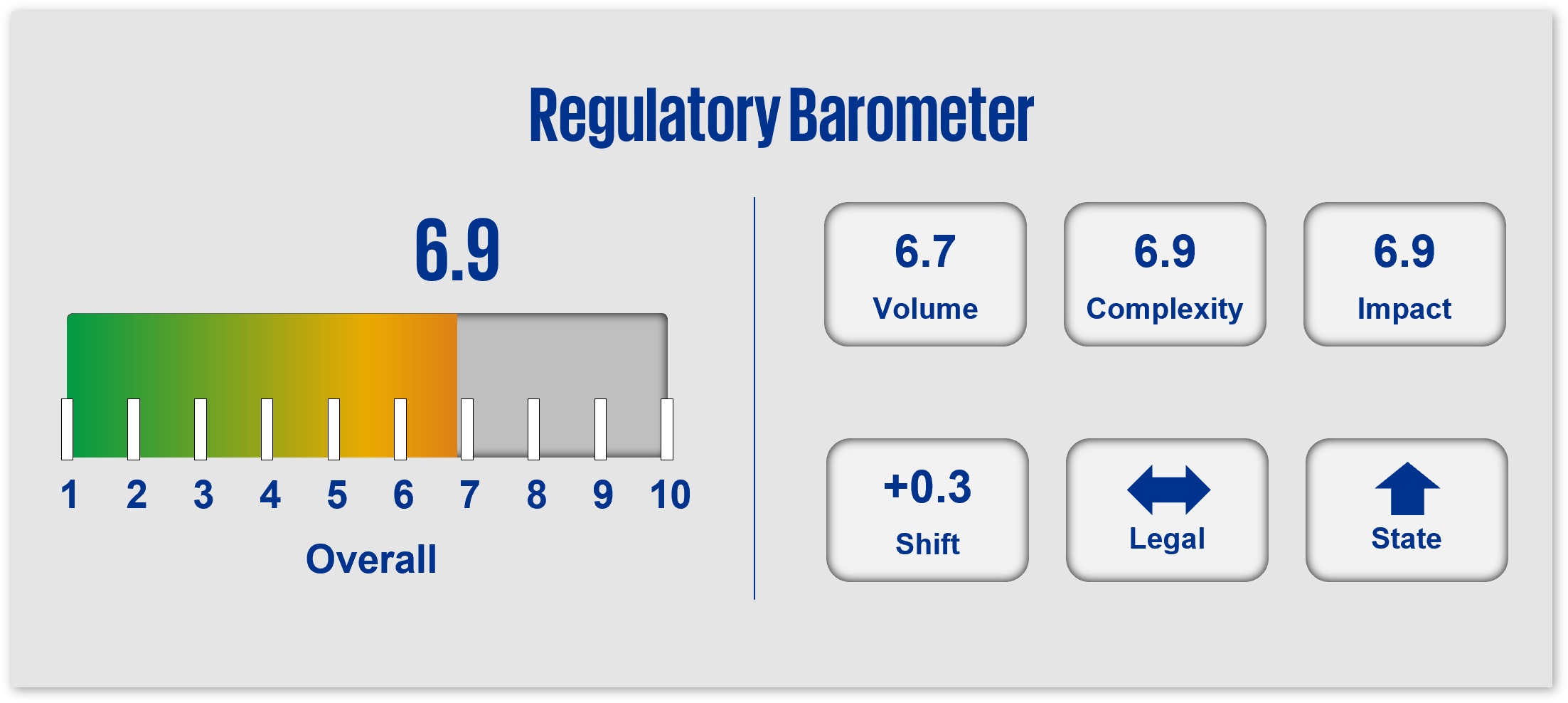
Nationwide consumer-reported fraud losses well exceed $10B annually, with regulatory alerts directly to consumers and companies being issued nearly every week. This, coupled with a new Administration focus on fraud, waste and abuse (particularly in/related to government spend), will help drive the focus in regulatory supervision of fraud model management, customer and party authentication, and investigation processes. Anticipate expanding attention in monitoring and reporting practices as well as regulatory policy and alerts in areas of both fraud management and consumer data, particularly in areas such as online privacy, cybersecurity, identify theft, and AI-generated deepfakes. Likewise, state requirements will continue to increase in such areas of AI, privacy and access, causing potentially divergent requirements.
1. Sizing Exposures
As advancements in technology continue to rapidly evolve so too do the risks of fraud and scams along with increasing and significant impacts to consumers, companies, and national security. The magnitude of these risks - and the ties with other risk areas such as cybersecurity, AI, and data privacy - will focus regulators on areas of expanding threat and vulnerabilities.
Key considerations in assessing sizing exposures involve:
Regulatory Focus
Across industries, regulatory agencies’ supervisory and enforcement activities are focused on mitigating expanding risks of fraud, waste, identity theft, and imposter and other scams, including those related to “predatory” pricing and payments. Regulatory expectations will include standardized processes and controls around access, authorization, data use, privacy, security, and sharing. Companies must continue to ensure the use of accurate data and controls to measure and manage risk exposure and reporting.
Data Sharing/Access
Given expansions to supply chains and arrangements with third parties and providers, regulators will have concerns for fraud risk as customer data potentially becomes more accessible across diverse platforms. To mitigate fraud and scams, risk management strategies must address vital areas such as large data models, third-party and affiliate data sharing, consent-based customer data sharing, payment verification procedures, and model development and validation.
Exposure Losses
The increasing volume and related costs of fraud and scams against individuals and businesses has led regulators to intensify their efforts to assess the breadth of fraud (e.g., numbers of individuals and/or products impacted) and impact severity through enhanced risk and fraud model management including considerations across:
- Existing and new products or services (e.g., digital assets, AI use and misuse (such as deepfakes)).
- Data privacy/information security (e.g., SpearPhishing threats, account takeovers).
- Consumer/investor protections and demographics.
- Types of fraud and scams (e.g., check, healthcare, synthetic identity frauds, and romance scams).
- Geographic operations.
2. Identification & Tips
Acting quickly and decisively to prevent, detect, and respond to fraud and misconduct concerns is essential to minimize disruption and loss. Anticipate increased regulatory attention to fraud identification, oversight, investigations, and mitigation.
For example, regulators will evaluate companies’ activities related to:
Identification/Tips
Identification and escalation of potential cases of fraud, through active monitoring of:
- Fraud reports received from employee and vendor hotlines.
- Alerts generated by surveillance systems and models/thresholds.
- Investigations reports related to non-compliance with guidance and regulations (e.g., market manipulation, red flag indicators, securities registration, telemarketing sales).
Complaints Management
Ongoing and thorough reviews of customer complaints management with a focus on issues identification including trends/fact patterns, escalation, investigation, and resolution. Within the fraud and investigations management processes, regulators will evaluate the timeliness, substance, and completeness of responses/remediation to customer complaints, claims, and disputes as a measure of “fair treatment”. They will also consider the clarity of consumer communications, including what is reimbursable as well as the consistency of responses and/or remediation between consumer groups. Key areas will include:
- Data sharing (e.g., use in large data models, sharing with third parties and affiliates, customer permissioned sharing (and new open banking rules)).
- Authorization/authentication procedures/protections.
- Account holds and freezes.
- Identity fraud (e.g., imposter scams, synthetic identity fraud).
Enhanced Oversight
The effectiveness of risk and compliance oversight of fraud and coordination across the AML/CFT, cybersecurity, and fraud functions. Regulatory attention will also focus on demonstratable, effective Board oversight and the implementation of threat detection/ monitoring processes that include:
- Maturity of endpoint detection and monitoring solutions.
- Coverage of threat intelligence (both on premises and cloud environments).
3. Internal Controls
To safeguard against fraud and other scams, as well as ensure consumer/investor protections, companies must establish effective internal controls for monitoring, detecting, and mitigating the attempts of threat actors.
Expect heightened attention to processes and controls relating to:
Authorization
Consent management and customer authentication requirements, such as multifactor authentication, password protection, one-time passwords, biometrics, third-party access, tokens, and peer-to-peer platforms. Implementing safeguards and controls in these areas, aids in the prevention of unauthorized use of sensitive information as it creates barriers for illicit activities.
Risk Management Program
Updates to fraud risk management programs to keep pace with evolving threats (in addition to effective internal controls, fraud model development and use, and assessments of consumer impacts). Regulators are currently focused on enhancements related to:
- Reporting on more categories of fraud and scams.
- Defining and clarifying when customers can be reimbursed.
- Implementing risk programs to identify and mitigate fraud and scams directed at vulnerable consumer groups (e.g., elderly, military).
- Detecting threats and ongoing monitoring and testing of fraud surveillance.
Data and Reporting
Processes and controls to effectively track and trace customer and transaction data. Examinations and reviews of risk management programs will assess a company’s:
- Ability to trace and report on the relationship between data inputs, outputs and business processes, authoritative sources, systems of record, and systems of origin.
- Data quality management standards including accuracy and consistency in fraud models/surveillance.
- Established routines for data reconciliation/quality.
Resolution/Remediation
Regulators will continue to strongly encourage companies to bolster their risk mitigation and remediation efforts through self-identification, self-reporting, and accountability, as measures of responsiveness to:
- Fraud alerts.
- Customer complaints.
- Misconduct.
- Whistle-blower activities.
4. Actions
- Add analytics and automation to client and third-party onboarding.
- Aggregate data and reporting to have a single view of the customers o more effectively manage complex fraud activities and strike a balance between fraud controls and customer experience.
- Eliminate antiquated technology and evaluate/implement emerging regtech capabilities to enhance transaction monitoring.
- Enhance fraud models to align to consumer protection regulations, monitor for suspicious activities, and provide real-time notifications and alerts.
- Evaluate and enhance, as needed, processes for sharing information real-time across departments (e.g., fraud, cyber, disputes).
- Establish a mature conduct risk program.
- Strengthen controls in regulatory focal areas (e.g., FinCEN priorities).
- Implement strong IAM strategies, including PAM and MFA, to secure access to critical customer systems and data. Regularly review access privileges.
- Integrate BSA/AML requirements into KYC processes.
- Conduct dynamic skills assessments of staffing needs for day-to-day operations of fraud monitoring/identification, investigations, and escalations. Enhance processes and sharing of information real-time across departments (e.g., fraud, cyber, disputes).
- Develop and promote customer education and awareness campaigns.
Dive into our thinking:
Get the latest from KPMG Regulatory Insights
KPMG Regulatory Insights is the thought leader hub for timely insight on risk and regulatory developments.
Explore more
Meet our team





