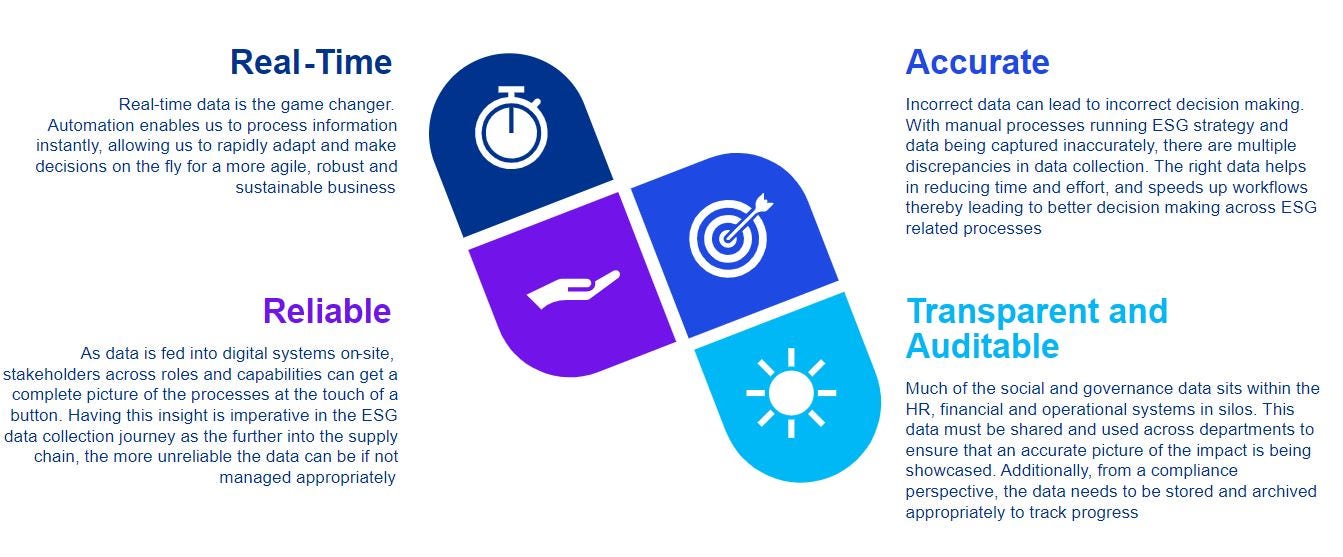
In today’s dynamic business landscape, the imperative to incorporate environmental, social and governance (ESG) considerations into corporate strategies has become increasingly apparent. As global awareness of climate change, social inequalities and ethical business practices grows, businesses are recognising that addressing ESG factors is not only a moral obligation, but also a strategic necessity all through the value chain. Embracing sustainability practices, fostering social responsibility, and upholding strong governance standards are integral components of contemporary business plans, ensuring long-term resilience and relevance in a world where stakeholders demand more than just financial success.
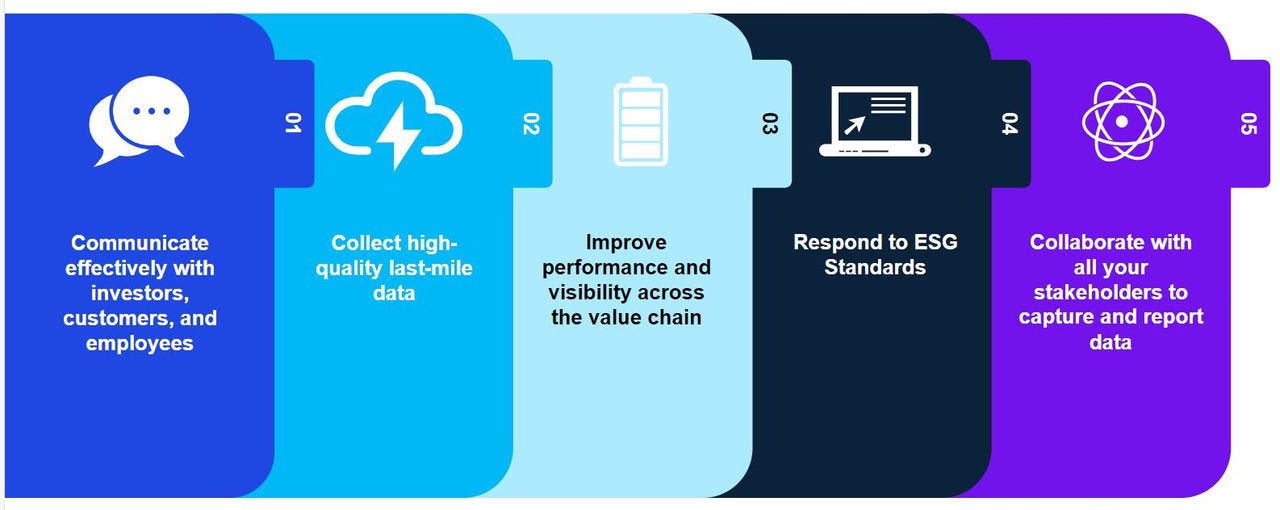
Global Capability Centres have the opportunity now to play a pivotal role in the overall ESG journey of a company.