The perfect way to strengthen trust, acquire customers and guarantee the success of Open Banking initiatives is to implement an efficient internal control framework coupled with continuous assessment of the operational effectiveness of the Open Banking model. In order to limit the risks and be able to comply with strict regulations, banks and external financial service providers need to design and build strong internal control frameworks around their Open Banking environments. Open Banking is an evolution towards an environment in which both financial and non-financial services and data are integrated into complete customer pathways that are personalised and geared to the customer’s requirements. Customer service will be addressed by multiple parties concurrently. The transparency of this kind of collective approach is expected to encourage competition and innovation in the European financial sector.
As a result, consumers will have greater choice and at the same time their high expectations, inherent in the digital era, will be met. The PSD2 banking legislation will drive a much bigger Open Banking movement. The description of Open Banking can sound intimidating for banks and customers, because Open Banking can be viewed as opening the door to security and privacy risks, as well as operational and reputational risks. Precisely for that reason, it is essential that Open Banking is preceded by buy-in from the customer. We at KPMG can help banks and other companies whose business models are built around Open Banking to strengthen and retain that trust.
Open banking and customer buy-in
The Open Banking environment is a platform for different parties, such as financial institutions, external suppliers, customers, regulators and public authorities. On this platform, they come together and improve their services to consumers. If institutions want to succeed in Open Banking, they will have to address the crucial element of ‘trust’ and secure customer buy-in. Let us take a look at a few important factors that can influence customer buy-in:
- Customers will have to enter into new relationships of trust with less familiar third parties. Customers will have to give their permission to make their data available;
- New phishing techniques - Cyber criminals and other malicious parties will probably have more opportunities to threaten bank customers, at least in the initial phase of Open Banking, given the fact that customer data will be released outside the conventional banking system, endangering the security of the data;
- Exposure of personally identifiable information (PII) in the communication between older systems and APIs. If PII data are handled inappropriately, banks and external financial service providers will be vulnerable to security and privacy risks.
KPMG recognises these challenges that banks and third parties will face in the future and has developed an effective framework to limit those risks. Organisations can benefit from KPMG's expertise in the areas of risk management, privacy and security, allowing them to increase trust and encourage their customers to embrace Open Banking.
Open Banking in Control framework
Open Banking is here to stay. Building a strong control framework right from the start will speed up your organisation’s Open Banking pathway in a controlled manner. KPMG's Open Banking in Control framework considers 10 critical building blocks of the Open Banking model (see figure 1) from a risk management perspective. By systematically addressing the controls built up around each of the 10 elements of Open Banking, banks and external suppliers benefit from a complete and strong control environment that limits privacy and security risks. Depending on which phase the Open Banking initiatives within your company are in, KPMG can help you evaluate the maturity of the internal control framework or help you build up and implement the internal control framework for Open Banking.
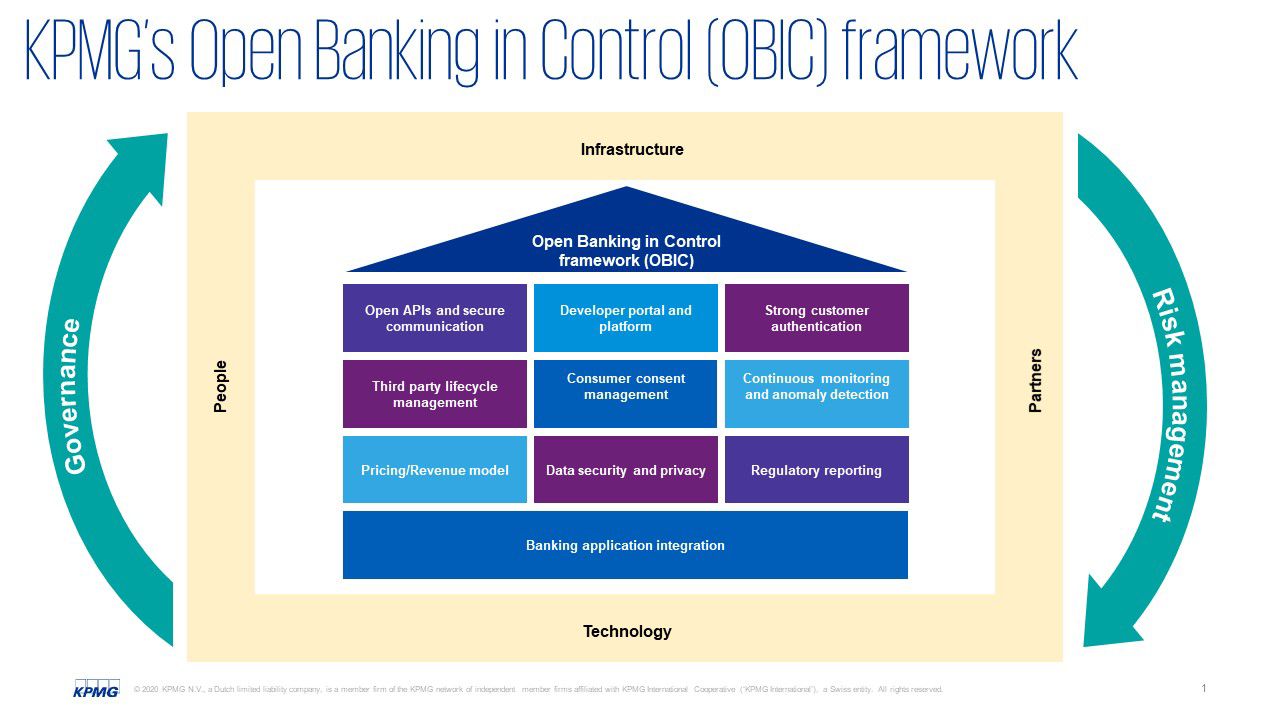
Open Banking in Control framework assessment
Traditional governance, as it has existed in organisations for many years, could impede the progress of Open Banking rather than support its development. Open Banking calls for a governance framework that aligns people, partners, technology and infrastructure. Open Banking is associated with a number of inherent risks. In order to succeed in Open Banking, a strong internal control framework is therefore vitally important. It is possible that conventional risk analyses and internal control models will not sufficiently cover all the specific elements of Open Banking, such as data privacy, security and managing the life-cycle of third parties. Due to the risks associated with Open Banking, the requirements in terms of complying with the rules will be extensive and strict. Besides, compliance is always the top priority for the financial sector in order to win and retain customer trust.
Implementation of the Open Banking in Control framework
By providing access to data, products and services via Open Banking APIs, banks could experience a step-by-step impact in the long term that may cannibalise sales of their own products and services. On the other hand, third parties and PSPs, while they are using data, will need to tackle critical risks connected with the processing of information. KPMG can support you by means of a risk index that gives you in-depth insight into building a strong control framework. An element-specific risk index, a general risk index or a risk index for the short and medium term will offer you valuable insights in order to limit operational and reputational risks and at the same time implement Open Banking initiatives.
A strong framework that addresses the Open Banking building blocks, as shown in figure 1, will ensure that you remain in control of the relevant aspects of regulations, compliance, risks, security and internal control and will promote flexibility and an informed risk appetite during your Open Banking project. Building a solid framework is the key to winning customers’ trust. KPMG can support you as a partner in implementing a strong control framework that speeds up your Open Banking project, reduces your time-to-market and helps you build a resilient, future-proof organisation.
Why KPMG?
KPMG has a long and proven record in the areas of IT auditing, operational reliability, risk management, cyber security and privacy. The core team behind Open Banking in Control consists of a wide range of experts: from data experts and IT auditors to cyber security & privacy experts, lawyers and ethicists. Moreover, with more than 155,000 colleagues in 144 countries, we always have the right expertise on hand to meet the specific requirements of each assignment.
The Open Banking in Control team works mainly for banks, innovative fintechs and external financial service providers. For example, we offer assurance about PSD2 (a driver of the Open Banking movement) for fintechs and software firms in order to strengthen their internal control environments and adapt them to the new regulations.
If an external supplier wants to secure the trust of customers by embracing Open Banking and building innovative solutions, while simultaneously complying with the requirements of regulations, a strong internal control environment is a must. And if Open Banking is one of the most important value propositions on the digital transformation agenda within financial services, it is time for companies to design and build internal control frameworks that limit the inevitable risks of Open Banking.
We have the expertise and skills to help them do that. If you would like to share ideas with an expert in the field of Open Banking, please contact Paul Kromhout, director Risk Consulting Financial Services.


