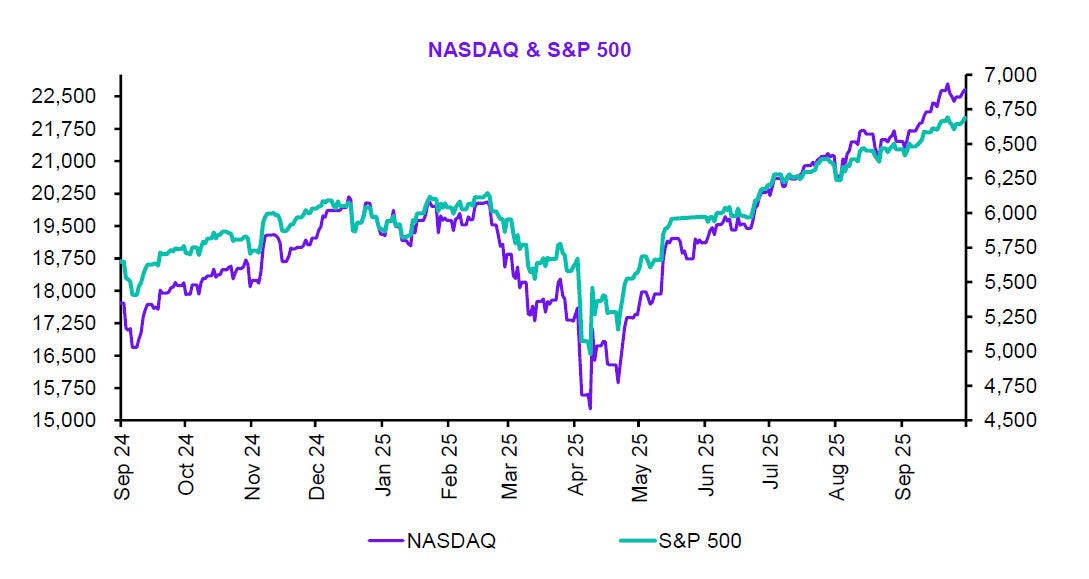
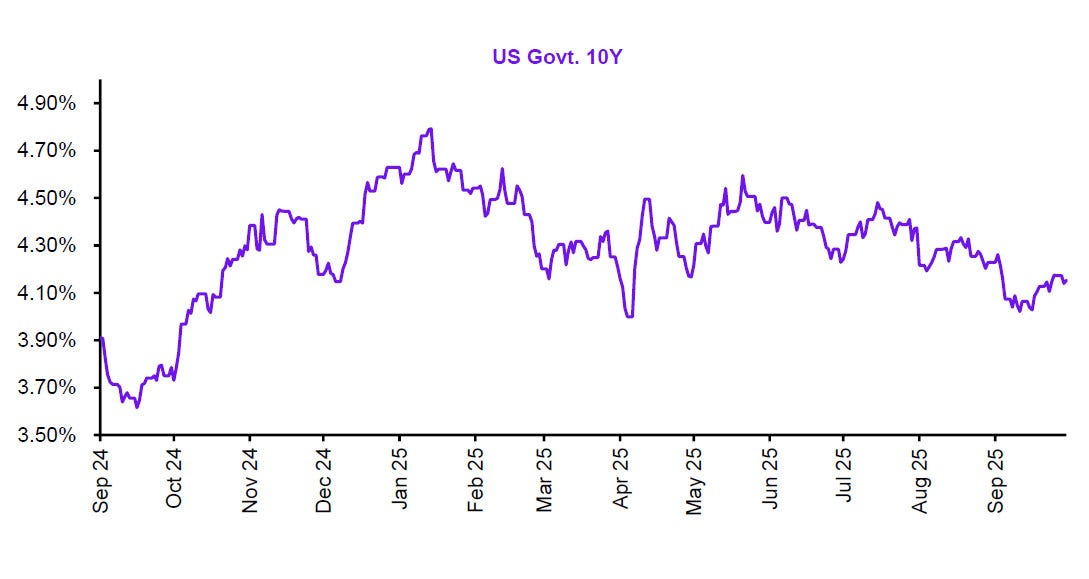
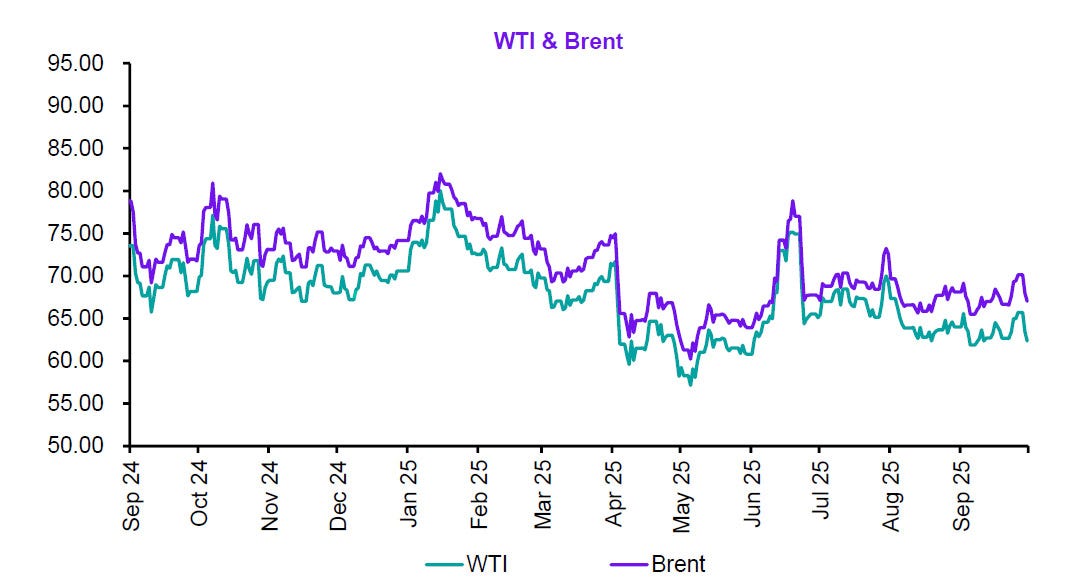
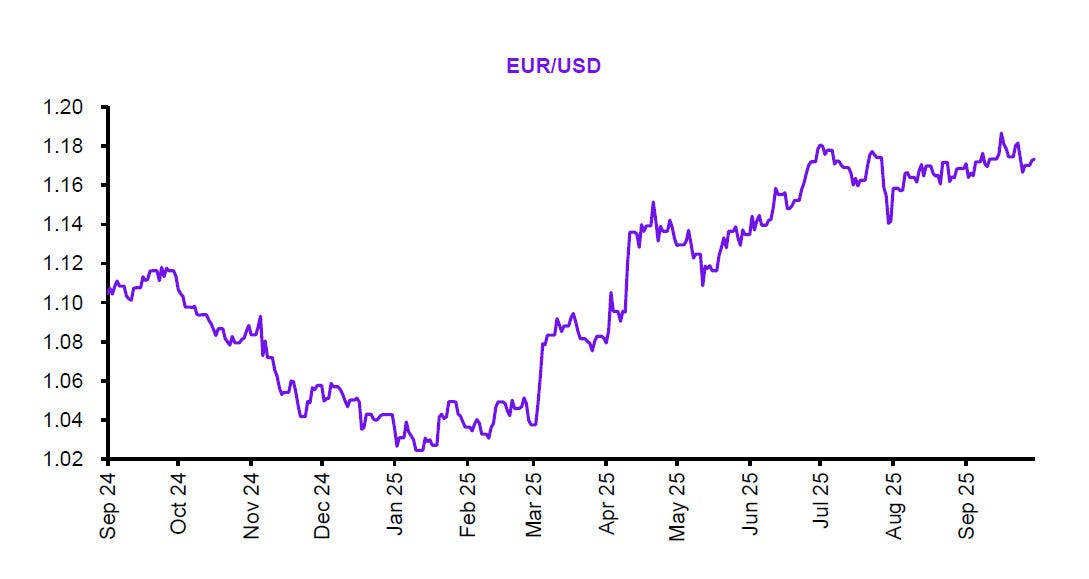
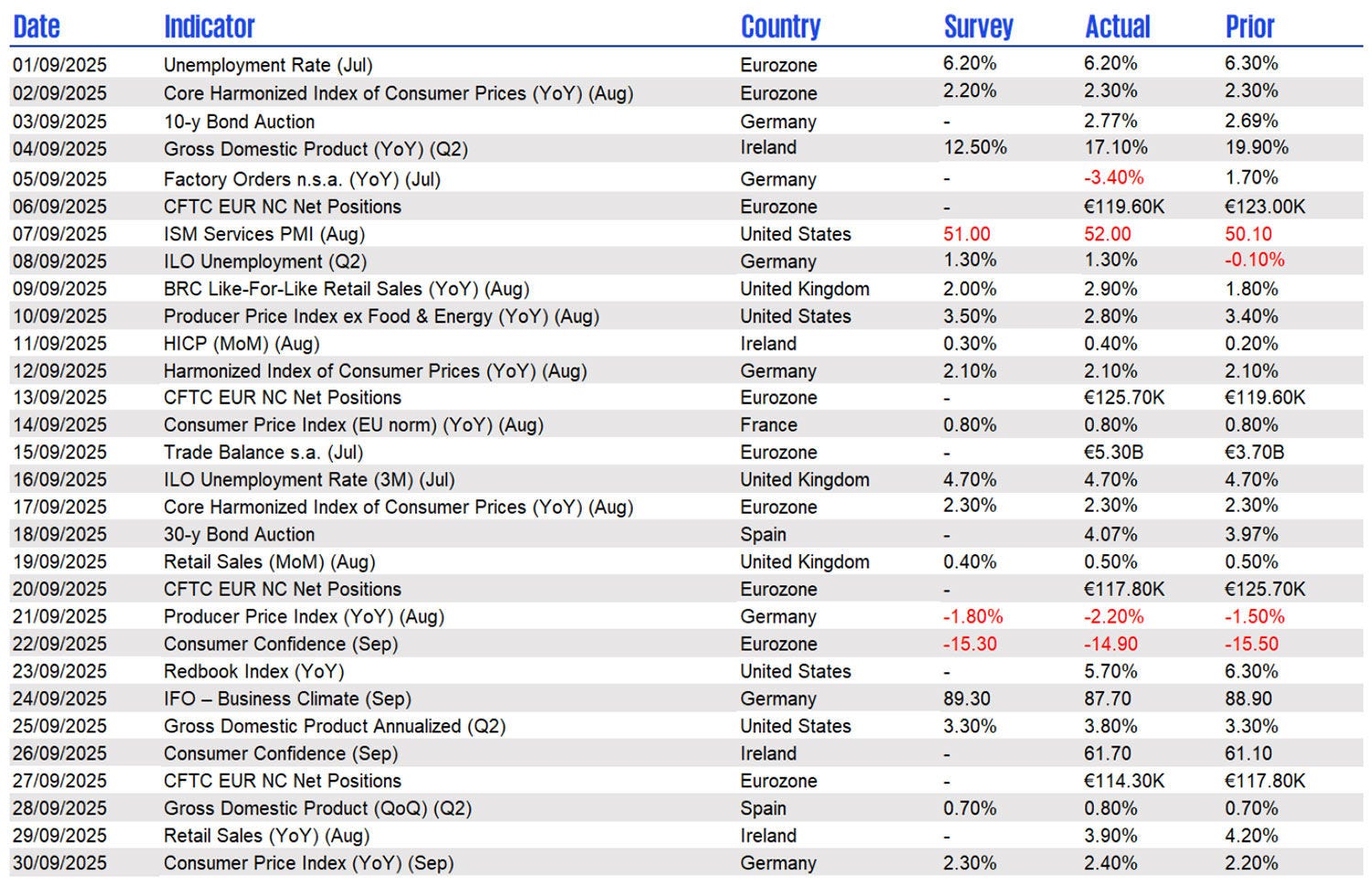
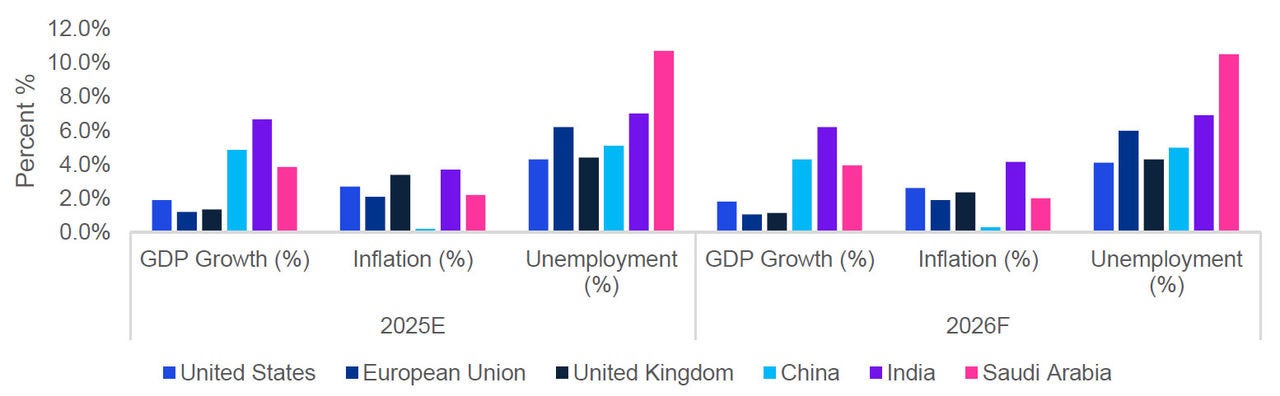
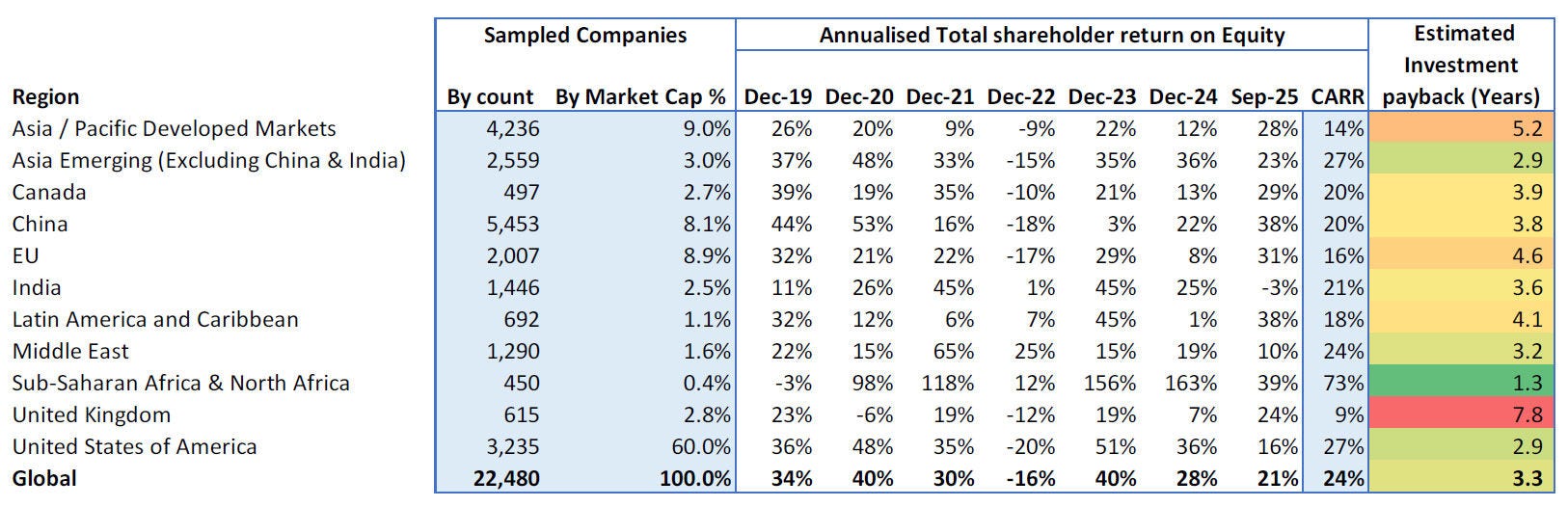
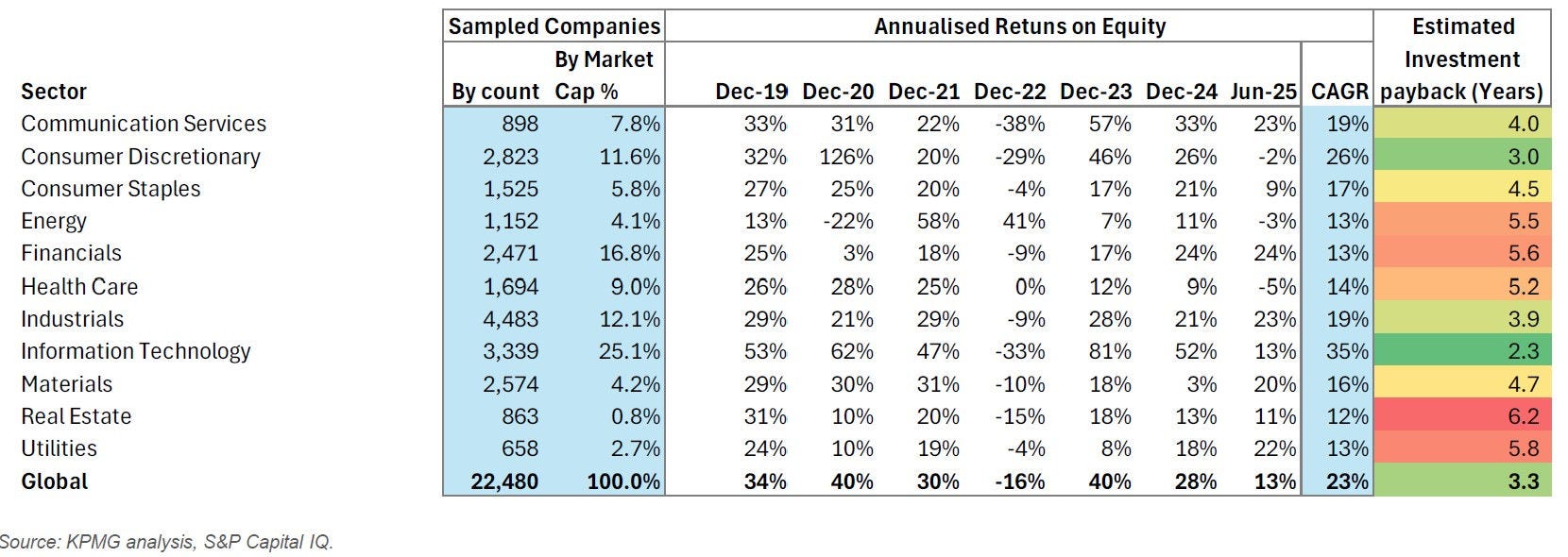
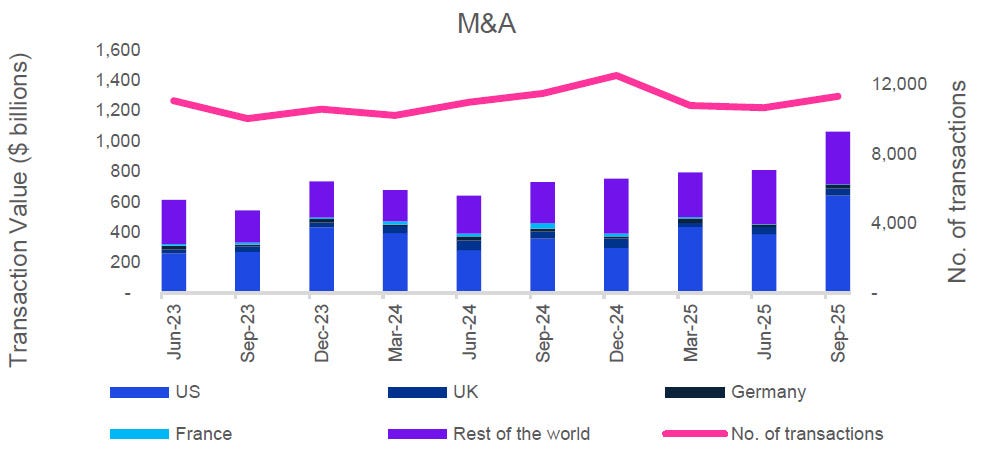
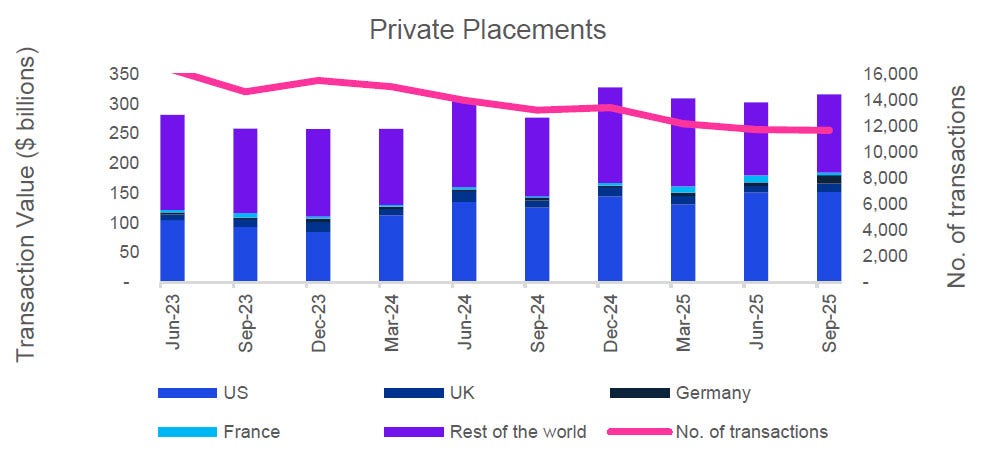
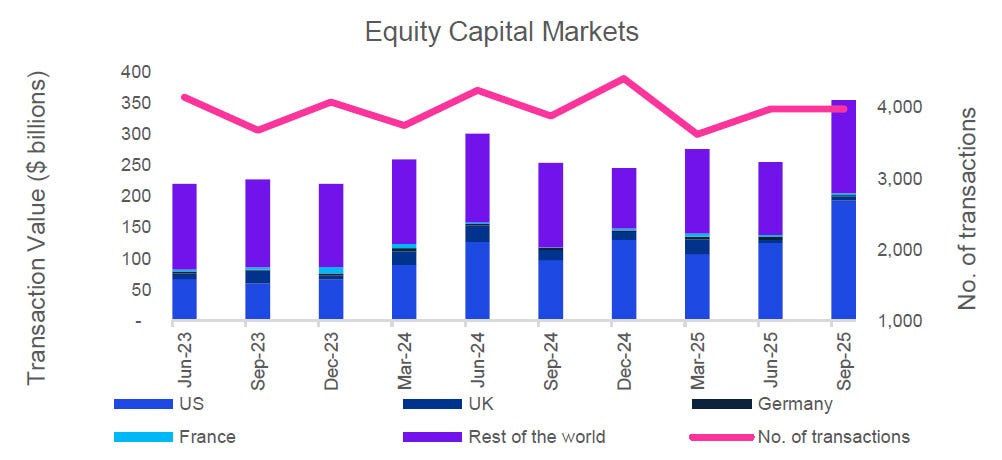
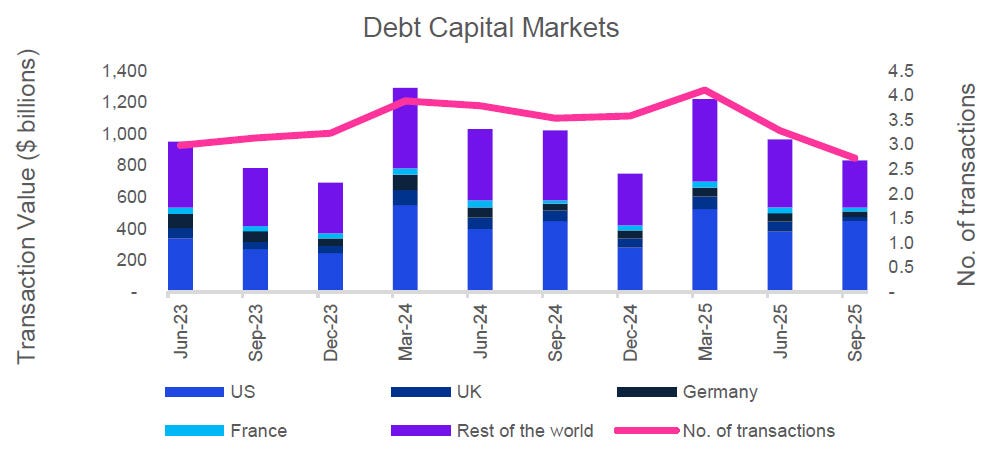
Global markets in September 2025 sustained their recovery momentum, buoyed by signs of stabilised inflation, resilient consumer demand, and eased energy prices.
Equities advanced modestly, while bond yields declined amid expectations of gradual rate cuts by major central banks. Investor sentiment improved, though regional divergences in growth and persistent geopolitical tensions continue to shape global risk appetite.
At a macro level, Europe’s industrial output rebounded, supported by stronger exports and fiscal measures in key economies. The U.S. labour market cooled slightly, offering reassurance on inflation trends, emerging markets saw renewed investor interest as a weaker dollar spurred fresh portfolio inflows.
Inflation moderated to 2.7% in the Eurozone and 3.4% in the UK, resulted in expectations of rate stability through year-end.
On the regulatory front, ESMA advanced work on green bond standards and MiCA implementation, underscoring continued focus on transparency and sustainability in financial markets.
For investors, this landscape continued to favour quality, resilience, and long-term structural themes. Valuations held steady, credit spreads tightened slightly, and real assets such as infrastructure and renewables maintained their premium. Companies with stable earnings, lower macro sensitivity, and reliable cash flows remain in demand.
The KPMG Financial Instruments (KFI) team have put together the insights below to provide an overview of the ongoing developments and to help you navigate through the changes.