KPMG in Greece, utilizing its in-depth knowledge of the Shipping sector and aiming to create added value, through the survey “The Future of Shipping” analyzes the seaborne trade, presents the role and viewpoint of the Greek shipowners in the global market, and remarks the impacts caused by economic, political and social changes. At the same time, it focuses on identifying new trends, development opportunities and challenges posed by the digital transformation, as well as on the pathway to "Green Shipping" based on global regulatory standards.
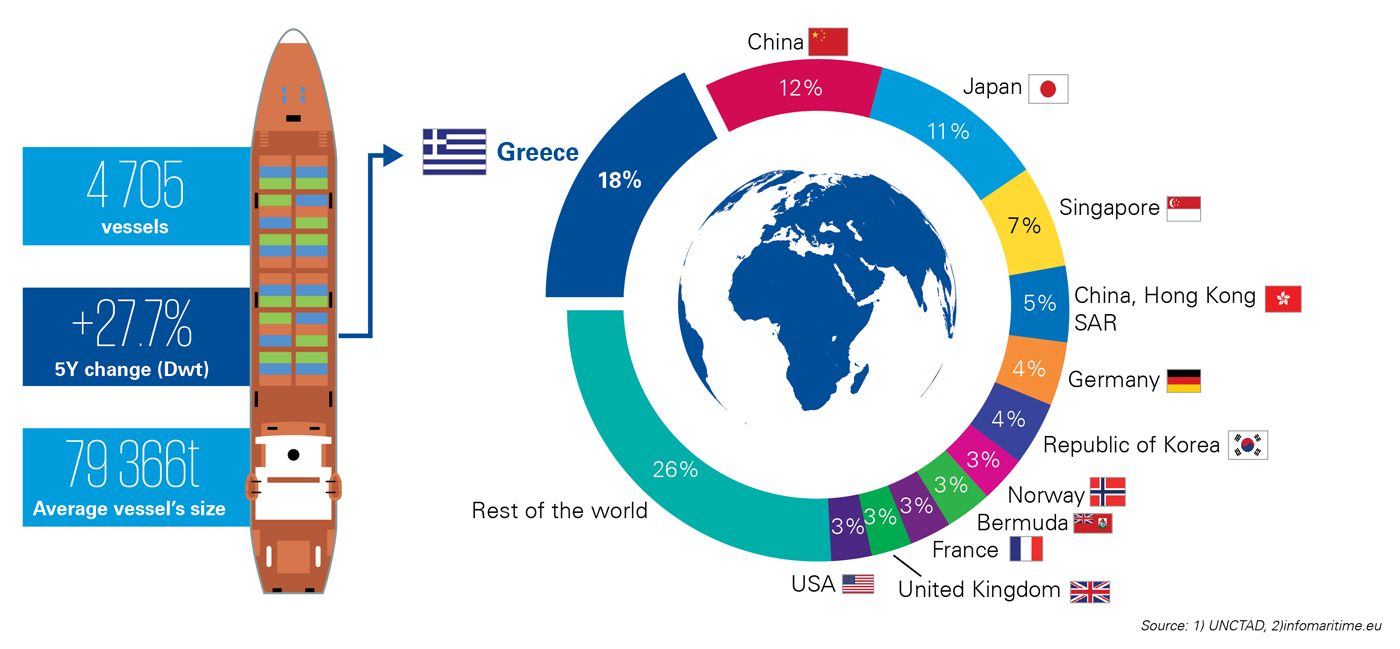
At present, approximately the 90% of world commodities’ trade (in terms of capacity) is seaborne, while the global fleet increased by 67% during the last decade. Specifically, Greece ranks 1st globally in ownership of merchandise vessels, presenting a 28% increase in owned capacity in the last five years, while the average vessel’s size is almost double, which indicates that Greek ship-owners mostly operate in high volume markets. Also, recent data show that Greek ship-owners are heavily investing in growing their fleets with new buildings, maintaining the average age of Greek-owned fleet’s lower than the global average.
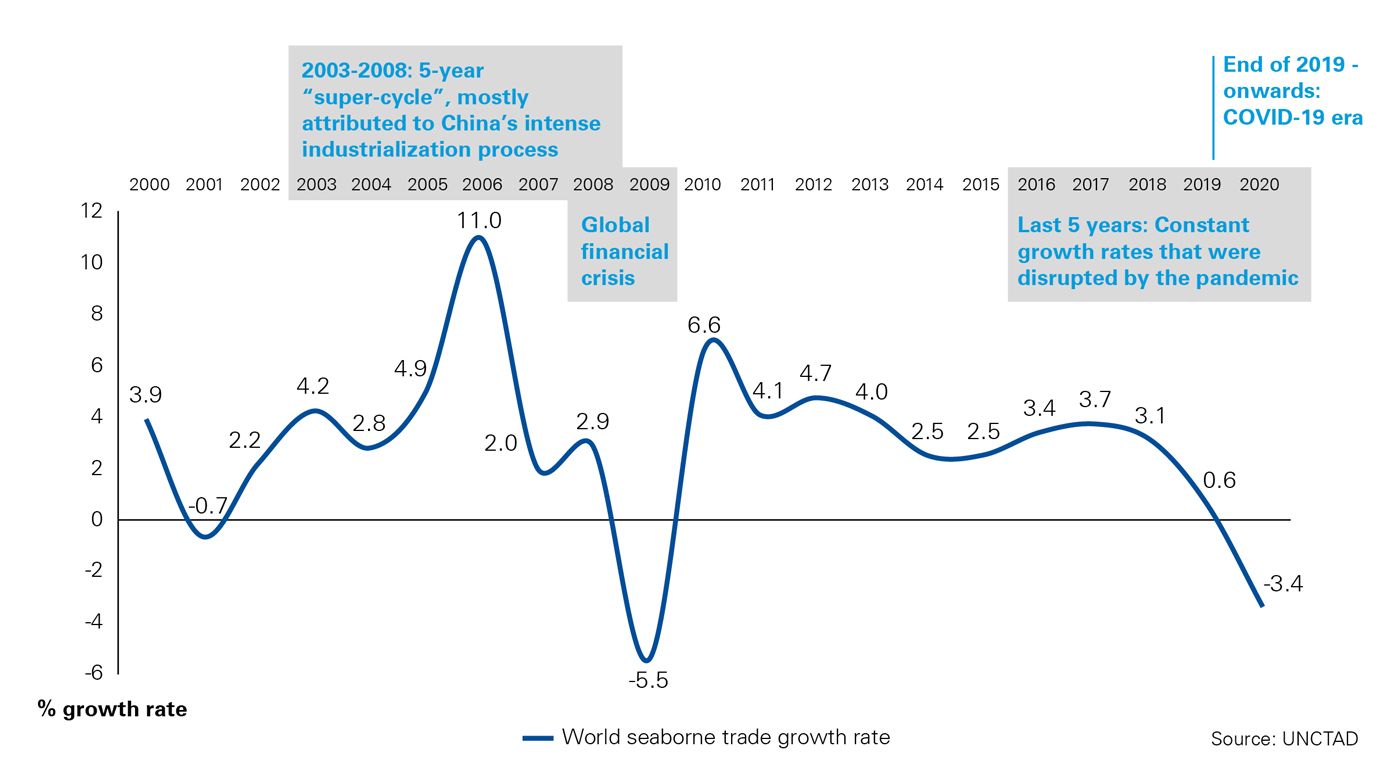
Sector’s historical growth is strongly related to the changes of global world stage, affecting directly the demand for shipping services. Since 2020, the increased demand for manufactured products during the COVID-19 era, has led to a sharp rise in the container and dry cargo freight rates, breaking the BDI and FBGCI records of the last 10 and 13 years, respectively. On the contrary, Tanker freight rates were reduced by almost 50% just a few months after the first lockdowns.
At the same time, the shipping industry presents new trends and challenges related to the development of technology. Firstly, the importance and implications emerge of the relatively recent compliance regulatory framework aimed at minimizing sulphur emissions emerge. In addition, the 400% increase in cyber attacks due to COVID-19 brings to the fore the use of new technologies, aiming at improving cyber security. The performance of the shipping industry is due to multifactorial conditions that are influenced by external components, so the question arises of the search for alternative ways of financing as well as an immediate and efficient response to the risks that arise. Finally, a challenge for the industry is the forces of supply and demand, as the oversupply of ships implies a percentage reduction in the cargo and freight market.
The digital transformation of shipping certainly stands out as the main trend of the industry and is an answer to several challenges. Technology solutions come to optimize operations, efficiency and add value to shipping companies in many ways.
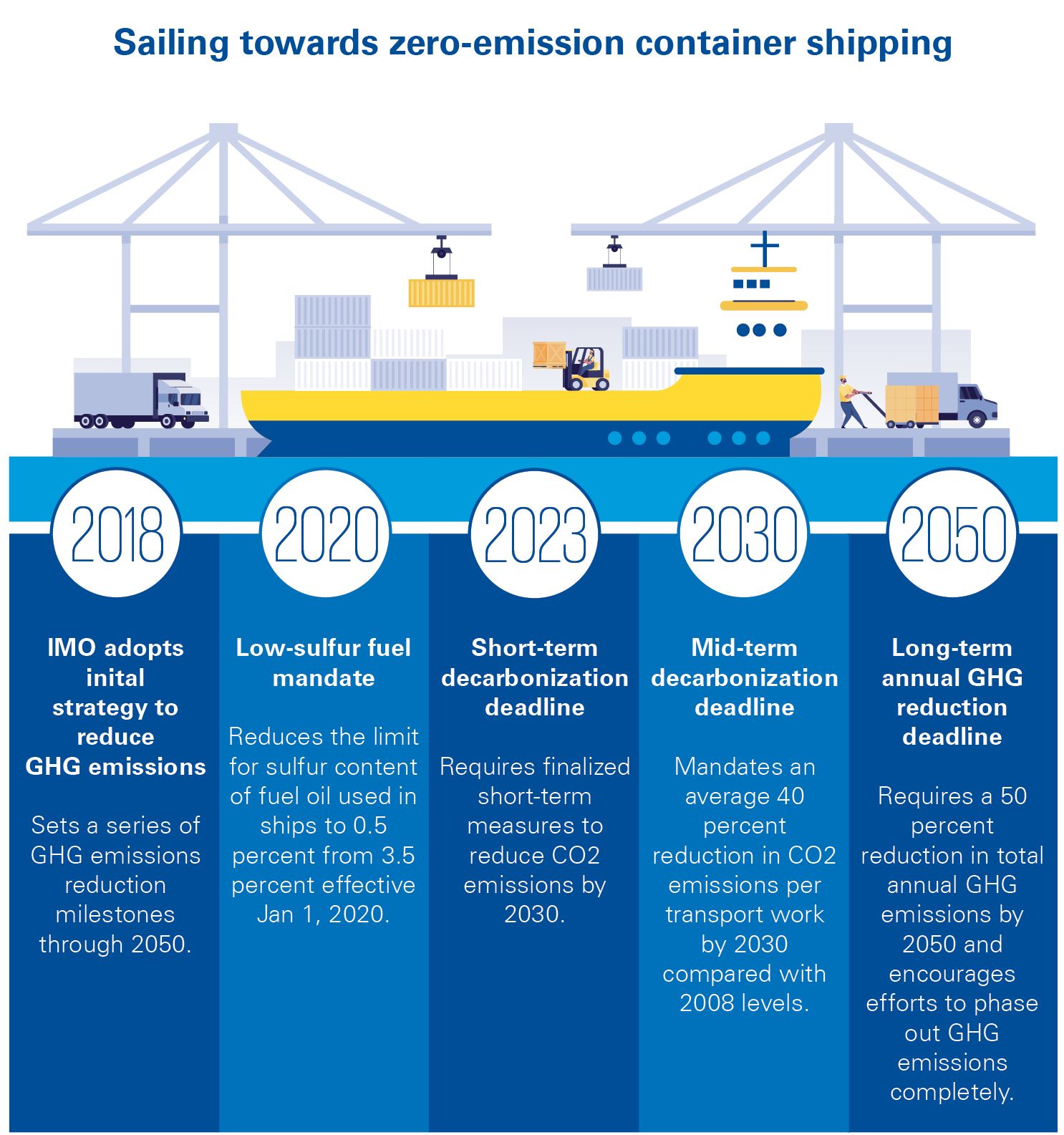
The intense climate change and the greenhouse effect due to anthropogenic gas (GHG) emissions have led to the creation of international treaties and regulations to ensure the safety and sustainability of the marine environment in the shipping industry. The International Maritime Organization (IMO), since 2008 has developed a vision and actions on greenhouse gas emissions internationally aiming to reduce by 50% and 70% of carbon by 2050, while also taking action to reduce greenhouse gases, disasters caused by maritime transport. In the framework of "Green Shipping", 7 milestones have been recognized, which are related to regulatory principles of energy-efficient operational ways, the development of alternative fuels, use of efficient technology, transparency and accuracy of data, "sustainable investment", carbon pricing policy and sustainability in each shipping business plan.
Michalis Papageorgiou

Director, Shipping Business Development Lead, Consulting, KPMG in Greece



