As threats to essential services grow more complex and interconnected, ensuring the resilience of critical infrastructure has never been more vital. The EU’s Critical Entities Resilience (CER) Directive is a major step forward in protecting vital sectors across Europe. Explore what the directive means, which sectors are affected, key compliance deadlines, and the practical actions organizations should take to get ready.
Connecting the CER and EU cyber rules for critical infrastructure
The CER Directive plays a foundational role within the broader EU cybersecurity regulatory framework for critical infrastructure. While the CER Directive focuses on strengthening the overall resilience of essential services, the remaining components of the framework specifically address cybersecurity protections against digital threats and attacks. Together, they form a complementary approach to safeguarding Europe's critical infrastructures, addressing both physical resilience and cyber risk. The interconnectedness of these frameworks underscores the EU’s comprehensive strategy for ensuring the security and continuity of vital systems.
CER
The Critical Entities Resilience (CER) Directive aims to strengthen the resilience of essential services and sectors, ensuring their continued operation during crises. Its impact on operational resilience includes increased risk management requirements, enhanced continuity planning, stronger governance, and mandatory reporting. The CER Directive raises the bar for operational resilience by ensuring that critical entities are better prepared, more accountable, and more integrated into a broader resilience framework.
NIS2
The Network and Information Systems Directive 2 (NIS2) strengthens EU-wide cybersecurity by expanding its scope to critical sectors like healthcare, energy, and public services. It aims to harmonize standards, enforce risk management practices, and mandate timely incident reporting. Key goals include improving supply chain security, enhancing accountability at the executive level, and fostering cross-border collaboration. The directive ensures a unified and resilient approach to addressing evolving cyber threats.
DORA
The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) is EU legislation that requires financial institutions to strengthen their operational resilience against ICT-related risks through measures for protection, detection, mitigation, and process recovery. The law entered into application on 17 January 2025.
CRA
The Cyber Resilience Act (CRA) is a new EU regulation designed to ensure safer hardware and software through mandatory cybersecurity requirements for manufacturers. The regulation entered into force in December 2024, with the main obligations applying from December 2027.
AI Act
The AI Act is the EU’s regulatory framework for Artificial Intelligence, aiming to ensure safety, transparency, and accountability. It classifies AI systems based on risk levels: unacceptable, high, limited, and minimal. The Act bans AI practices that threaten fundamental rights, like social scoring. It promotes trustworthy AI, requiring transparency for generative AI (e.g., ChatGPT). Companies violating the rules face hefty fines. The AI Act is the first comprehensive AI law, setting a global precedent for AI governance.
ISO 22301
This international standard enhances organizational resilience and is applicable to organizations of all types and sizes. It helps them better anticipate and respond to business continuity risks while also identifying opportunities for improvement more effectively.
Companies and sectors impacted
The CER establishes stricter resilience and security standards for entities deemed essential to society and the economy. Entities affected by the Directive are identified based on three main criteria:
- Criticality of services – providing services that are essential for the maintenance of societal functions, economic activities, or public safety;
- Sectoral importance – operating in key sectors such as energy, transport, healthcare, telecom, or water; and
- Interconnectedness – being part of systems whose failure could trigger widespread disruption across multiple sectors.

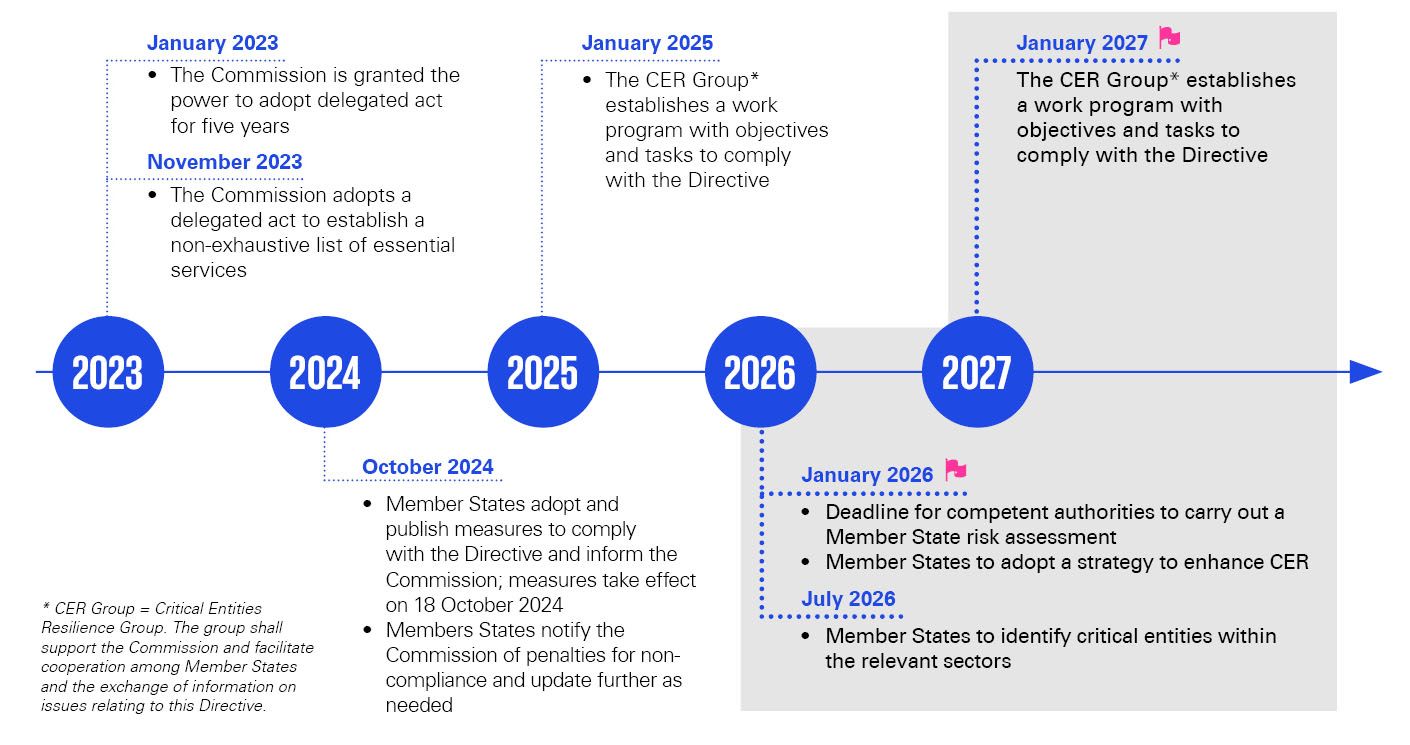
Implementation milestones
The process of identifying Critical Entities (CEs) under the CER involves several key milestones for member states. These milestones include conducting baseline assessments, sectorial analyses, risk identification, implement resilience measures, provide training and exercise, review and update the resilience measures taken. Compliance deadlines for CEs are structured to allow for phased implementation of resilience measures, testing, ongoing monitoring, and periodic reviews to enhance the security and reliability of critical infrastructure and essential services in Europe. By following these timelines and milestones, member states and designated entities can promote a culture of resilience and improve operational security across the region.
Deadlines for implementation
Preparing for compliance
As the CER Directive approaches full implementation, organizations have a valuable opportunity to proactively strengthen their resilience while ensuring future compliance. Although enforcement is not yet in effect, early preparation is crucial to minimize potential disruptions and meet regulatory expectations.
At this stage, identifying and leveraging synergies with existing compliance and security initiatives is key. Many organizations are already pursuing projects that align with other regulatory requirements or aim to enhance cybersecurity—these can serve as a strong foundation for CER readiness.
This forward-looking approach anticipates necessary changes, embedding compliance and resilience into transformation initiatives and represents an opportunity for entities to develop a holistic resilience strategy that addresses complex risks to critical infrastructure, improving defenses and response capabilities.
How KPMG can help
KPMG offers deep expertise in regulatory compliance and resilience, helping organizations navigate challenges such as risk assessment, operational resilience, and incident management. Our services are closely aligned with key EU cybersecurity regulations and now also cover the Critical Entities Resilience Directive.
By embedding CER requirements into your existing initiatives and taking early, proactive steps, you can enhance operational readiness, minimize disruptions, and protect your most essential services. With the right guidance, you can go beyond compliance—building long-term resilience.
There is more!
Download the full detailed document for a comprehensive look at the new CER2 Directive requirements, practical integration strategies, and insights into how KPMG can support your organization.
Authors - Elst Olivier, Partner & Benny Bogaerts, Partner
Explore
Connect with us
- Find office locations kpmg.findOfficeLocations
- kpmg.emailUs
- Social media @ KPMG kpmg.socialMedia




